Dec 7, 2024
5 Min

Aistra

As artificial intelligence continues to redefine industries and reshape human experiences, the adoption of Responsible AI is no longer optional—it's a strategic and ethical imperative. Organizations embracing AI must ensure that their innovations are trustworthy, transparent, and aligned with societal values. At the core of this journey lies the need for robust guardrails and adherence to evolving regulations like the European Union’s AI Act.
The EU AI Act, a landmark in AI governance, provides a framework for ensuring AI systems operate safely, ethically, and responsibly. Its guiding principles, such as Risk-Based Regulation and Fundamental Rights Protection, offer a roadmap for companies to navigate the complexities of AI adoption.
Let’s explore why responsible AI is vital and how these principles serve as the foundation for sustainable innovation.
Why AI Adoption Must Be Responsible
AI adoption is accelerating across industries, from healthcare to finance to retail. While the potential benefits are transformative, the risks associated with unregulated or poorly governed AI systems can have far-reaching consequences. Issues like biased algorithms, lack of transparency, and security vulnerabilities can erode trust, invite regulatory penalties, and even harm individuals and communities.
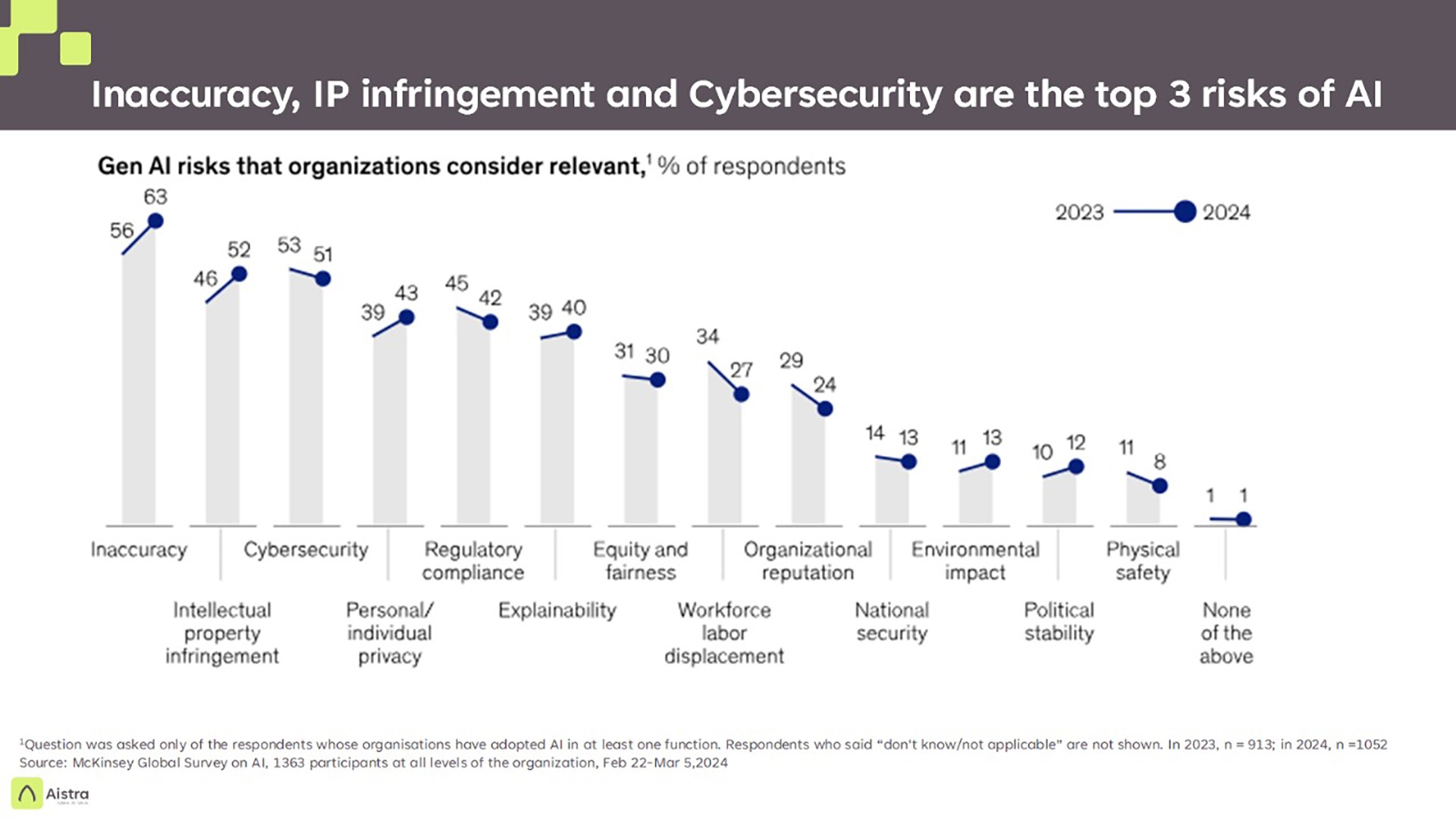
Responsible AI goes beyond compliance—it is about fostering trust among users, ensuring fairness, and mitigating risks. Companies that prioritize responsibility in their AI initiatives are better positioned to build long-term value, attract forward-thinking investors, and differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
The Role of Guardrails in AI Development
Building Responsible AI requires embedding guardrails at every stage of the AI lifecycle—from design to deployment and beyond. These guardrails ensure systems are developed with safeguards for fairness, security, and transparency, reducing the risk of unintended consequences. Techniques such as bias audits, privacy-preserving technologies, and robust security protocols are essential components of this approach.
By proactively integrating these measures, companies not only align with regulations like the EU AI Act but also demonstrate their commitment to ethical innovation.
Principles of the EU AI Act: A Blueprint for Responsible AI
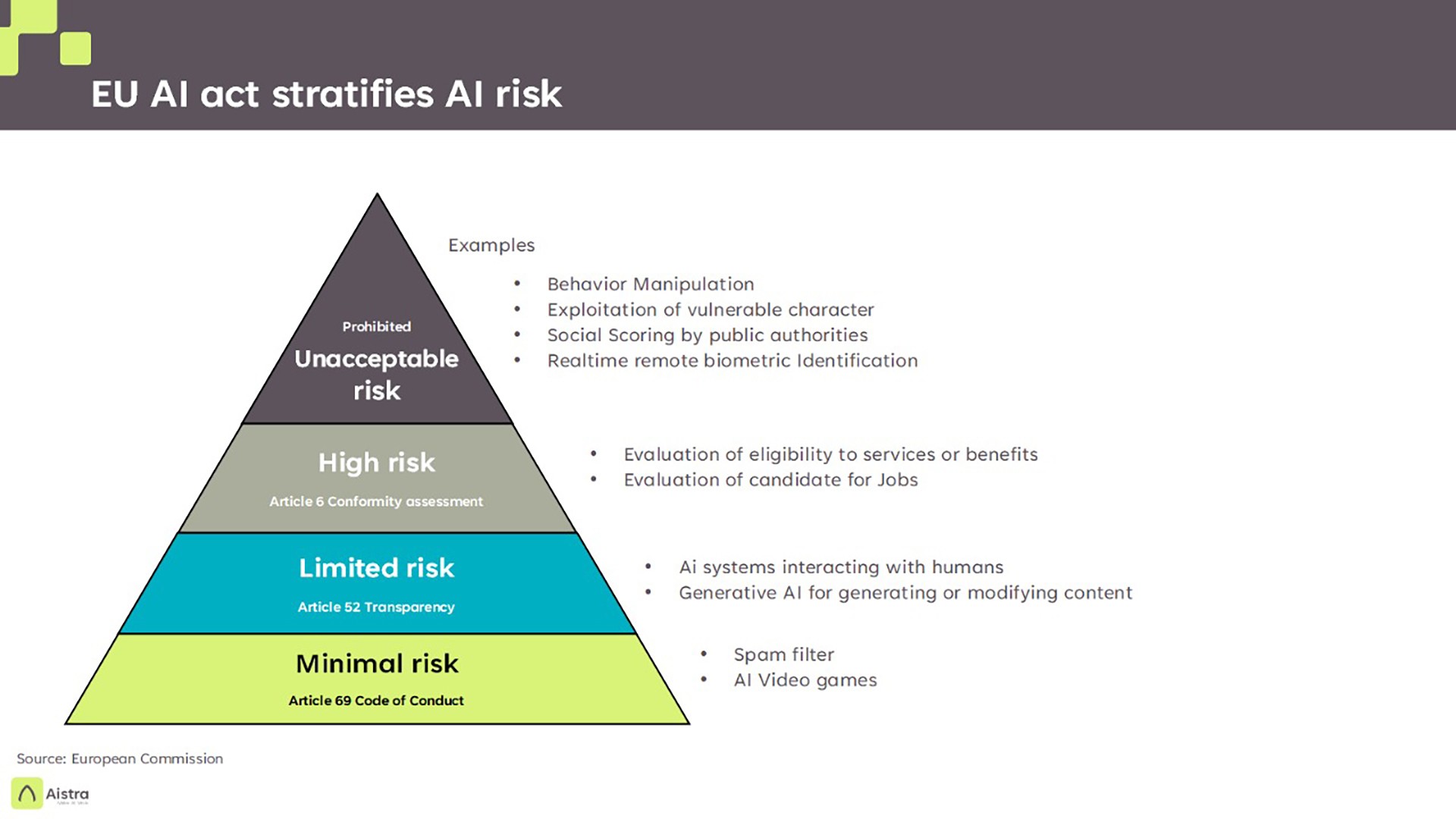
1. Risk-Based Regulation
The EU AI Act adopts a risk-based framework, categorizing AI systems into unacceptable, high-risk, limited-risk, and minimal-risk categories. Companies must prioritize compliance for high-risk applications, such as AI in healthcare, law enforcement, or recruitment. This ensures that the level of oversight corresponds to the potential harm the system could cause.
2. Fundamental Rights Protection
AI systems must respect fundamental rights, including privacy, non-discrimination, and human dignity. The Act places human welfare at the center of AI governance, preventing technologies that exploit vulnerabilities or undermine democratic principles.
3. Transparency and Explainability
Users and stakeholders must understand how AI systems work and the rationale behind their decisions. Transparency fosters trust, while explainability helps ensure that high-stakes decisions—such as loan approvals or medical diagnoses—are fair and justifiable.
4. Accountability and Oversight
The Act emphasizes the need for human oversight in critical AI systems. Developers and operators must establish mechanisms for accountability, conduct regular audits, and provide clear documentation to demonstrate compliance.
5. Robustness and Safety
AI systems must be technically robust and resilient to adversarial attacks or errors. This ensures that systems operate reliably under varying conditions and safeguards against unintended consequences.
6. Non-Discrimination and Fairness
The EU AI Act explicitly prohibits discriminatory outcomes from AI systems. Developers must address biases in training data and algorithms to ensure fairness, particularly in high-risk applications like hiring or law enforcement.
7. Data Governance
High-quality data is the foundation of ethical AI. The Act mandates secure and lawful data handling practices, emphasizing transparency in how data is collected, used, and shared.
8. Security and Privacy
AI systems must protect sensitive data against breaches and misuse. Techniques like differential privacy, encryption, and secure access controls help ensure compliance with privacy regulations and protect user trust.
9. Prohibition of Harmful AI Uses
Certain applications, such as social scoring or real-time biometric surveillance, are explicitly banned under the Act. These prohibitions safeguard against AI technologies that could undermine fundamental freedoms.
10. Innovation and Trust
The Act recognizes the importance of fostering innovation while maintaining trust. Initiatives like regulatory sandboxes allow companies to test AI systems in a controlled environment, promoting growth without compromising ethical standards.
Responsible AI is a Strategic Advantage
Responsible AI is not just about adhering to regulations; it’s about building systems that reflect the values of fairness, transparency, and accountability.
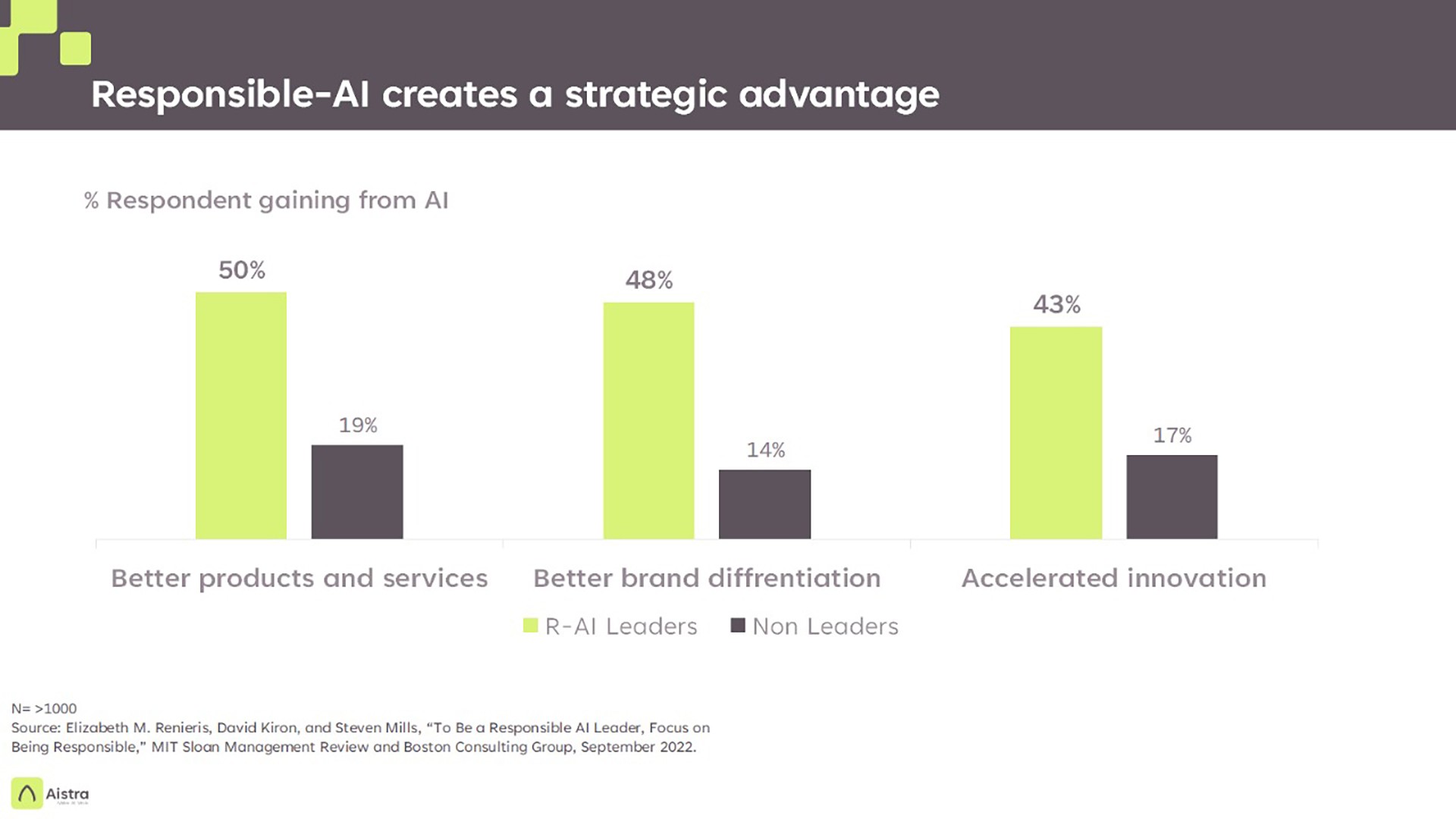
As AI becomes deeply integrated into business processes and everyday life, companies that prioritize responsibility will set themselves apart as leaders in ethical innovation.



